2024-03-22
Dettifoss │ Iceland Photo Gallery
Documenting Iceland
by: Rafn Sig,-
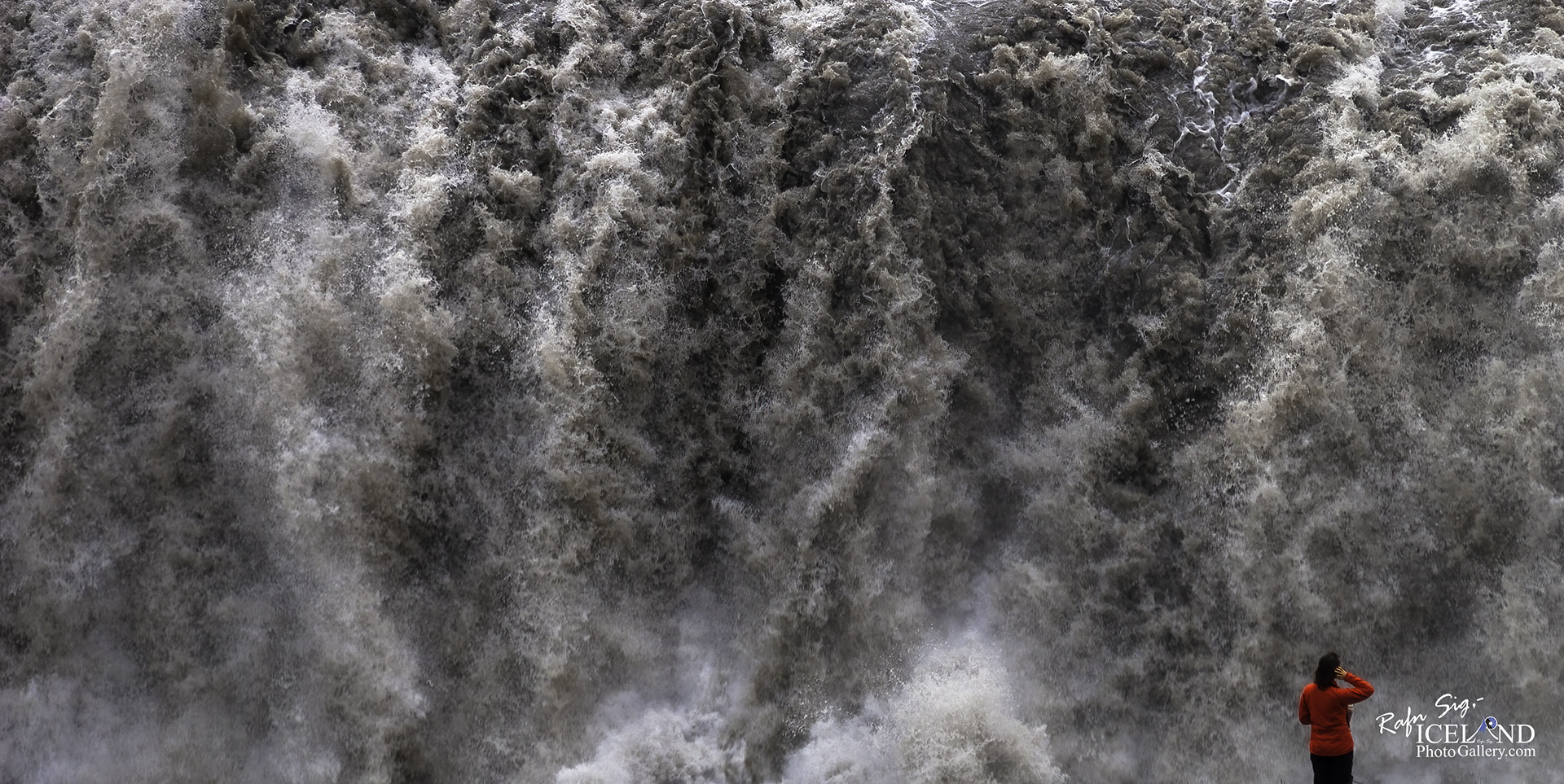

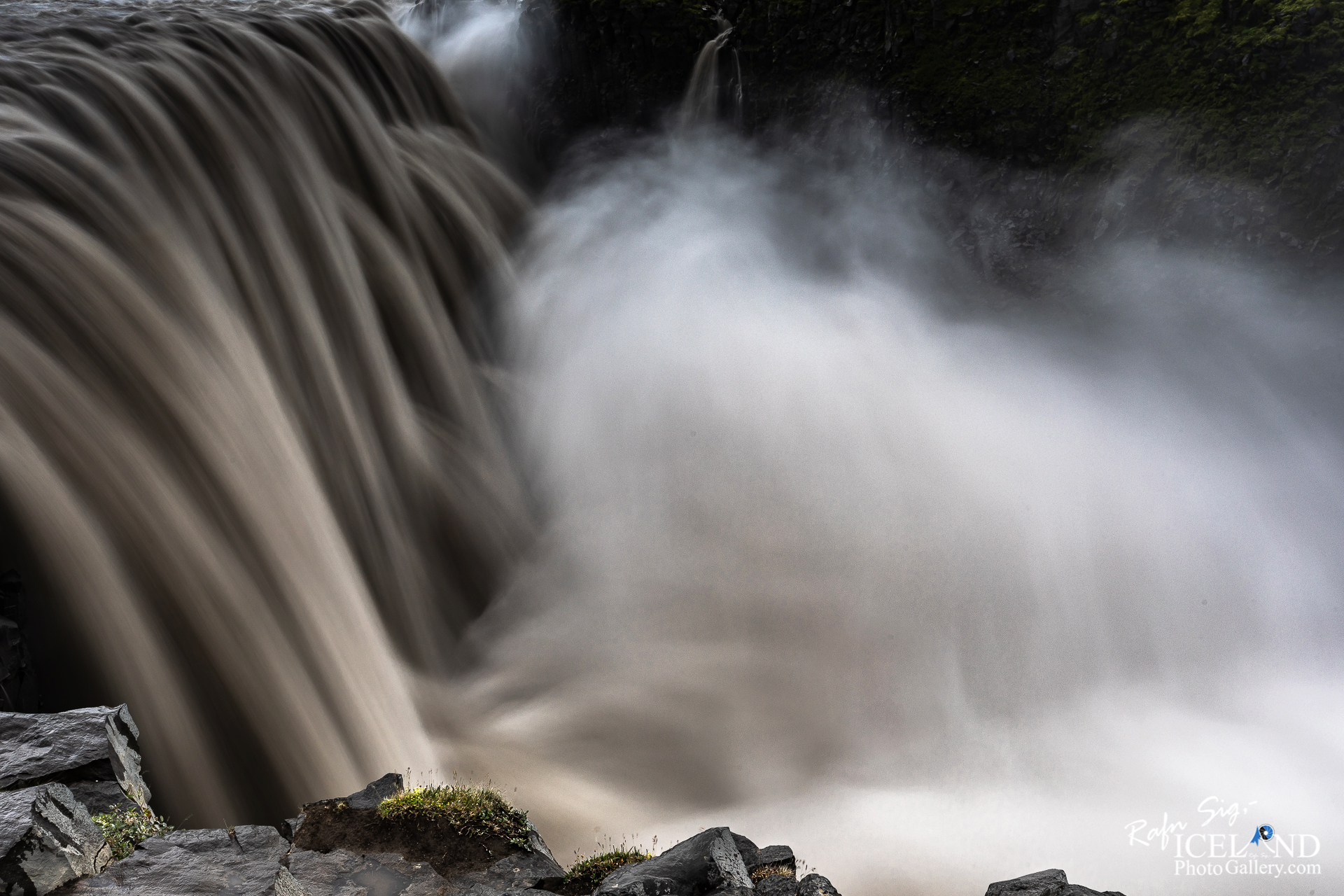
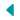
Dettifoss er talinn öflugasti foss Evrópu. Ógnarkraftinn má finna með því að leggja lófa við klappir nálægt fossinum og finna hvernig bjargið titrar. Fossinn er 44-45 m hár og um 100 m breiður.
Ísland er ungt land í jarðfræðilegum skilningi. Einkenni þessa unga lands eru meðal annars margir fossar sem enn hafa ekki náð að afmá stalla í farvegi sínum. Í Jökulsá á Fjöllum er einstök og heillandi fossaröð en fossarnir breytast smám saman, eða jafnvel hverfa, eins og fossum er eðlislægt að gera.
Jökulsárgljúfur eru þrengst, um 100 m breið, á stuttum kafla norðan við Dettifoss. Þessi þröngi, 500m langi bútur er verk Dettifoss, sem grafið hefur í landið með sínu daglega nuddi frá lokum hamfarahlaupanna. Stóru gljúfrin sáu hamfarahlaupin og jökulsá um að móta á síðustu árþúsundum.
Hugmyndir voru uppi um virkjun vatnsaflsins í gljúfrunum, en þær strönduðu á því að hraunlögin eru of gropin til að halda vatni í uppistöðulóni. Á austurbarmi Jökulsárgljúfra nálægt Hafragilsfossi er þversnið í gíg á gossprungu sem kennd er við Randarhóla.
Dettifoss is the most powerful waterfall in Europe. Its enormous power can be felt if you lay your hand on a rock close to the waterfall, it vibrates! The waterfall is 44-45 m high and about 100 m wide.
In a geological sense, Iceland is a young country. Among his young country’s characteristics are the numerous waterfalls that have not yet eroded the embankments in their path. Jökulsá á Fjöllum has a unique and fascinating series of waterfalls. Those waterfalls change slowly over time, and even completely disappear, which is a natural part of the lifetime of waterfalls.
Jökulsárgljúfur is the most narrow, about 100 m wide, in a short segment to the north of Dettifoss. This narrow, 500 m long stretch was made by Dettifoss, which has carved through the land with its daily erosion that has occurred since the end of the outburst flood from the time of the natural catastrophes. The large passes were shaped by the outburst floods and glacial river over recent millennia.
There were ideas about harnessing the power of the water in the passes, but these were abandoned due to the fact that the lava formations are too porous to hold water in a reservoir. On the east bank of the Jökulsá canyons, near Hafragilsfoss, a cross section of a volcanic fissure named Randarhólar exposes the feeder dike in the cliff wall.
. . . All info at: https://www.patreon.com/RafnSig
– 0 –
Viltu styrkja þessa síðu?
Vefsíðan Iceland Photo Gallery er unnin í sjálfboðavinnu. Ef þú hefur áhuga á að styrkja þetta framtak til áframhaldandi uppbyggingar er hægt að leggja inn á:
Reikningsnr.: 0101-26-013169
Kennitala: 310155-4469